Our treatments
As British GMC accredited and appraised urologists, robust governance is the cornerstone of their clinical practice along with compassion, communication and outstanding surgical care.
Treatment for LUTS and BPH
-

Life Style Measures
The initial approach in managing bothersome ‘waterworks’ lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) is to employ conservative measures including: fluid intake management, avoiding caffeinated drinks and pelvic floor exercises.
-
Medications
The choices of medication include; Alpha Blockers, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, Anti-cholingeric drugs, Beta3 agionist, Phosphodiesterase (PDE-5) inhibitors
-
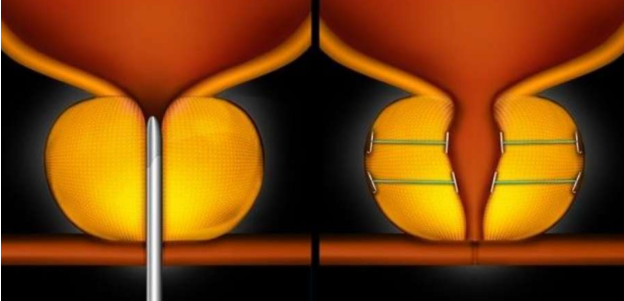
Urolift
The Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL) procedure uses the Urolift device. This device is the very latest non-invasive approach to treating symptomatic BPH. The device lifts or holds the enlarged prostate tissue out of the way so it no longer blocks the urethra. There is no cutting, heating or removal of prostate tissue.
-
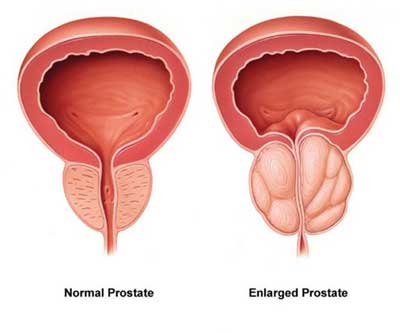
TURP
Under direct vision using a telescope passed down the water-pipe (urethra), small ‘chips’ are repeatedly cut away from the prostate, ‘boring out’ a wide channel, relieving obstruction to the flow of urine out of the bladder.
Prostate cancer diagnostics
-
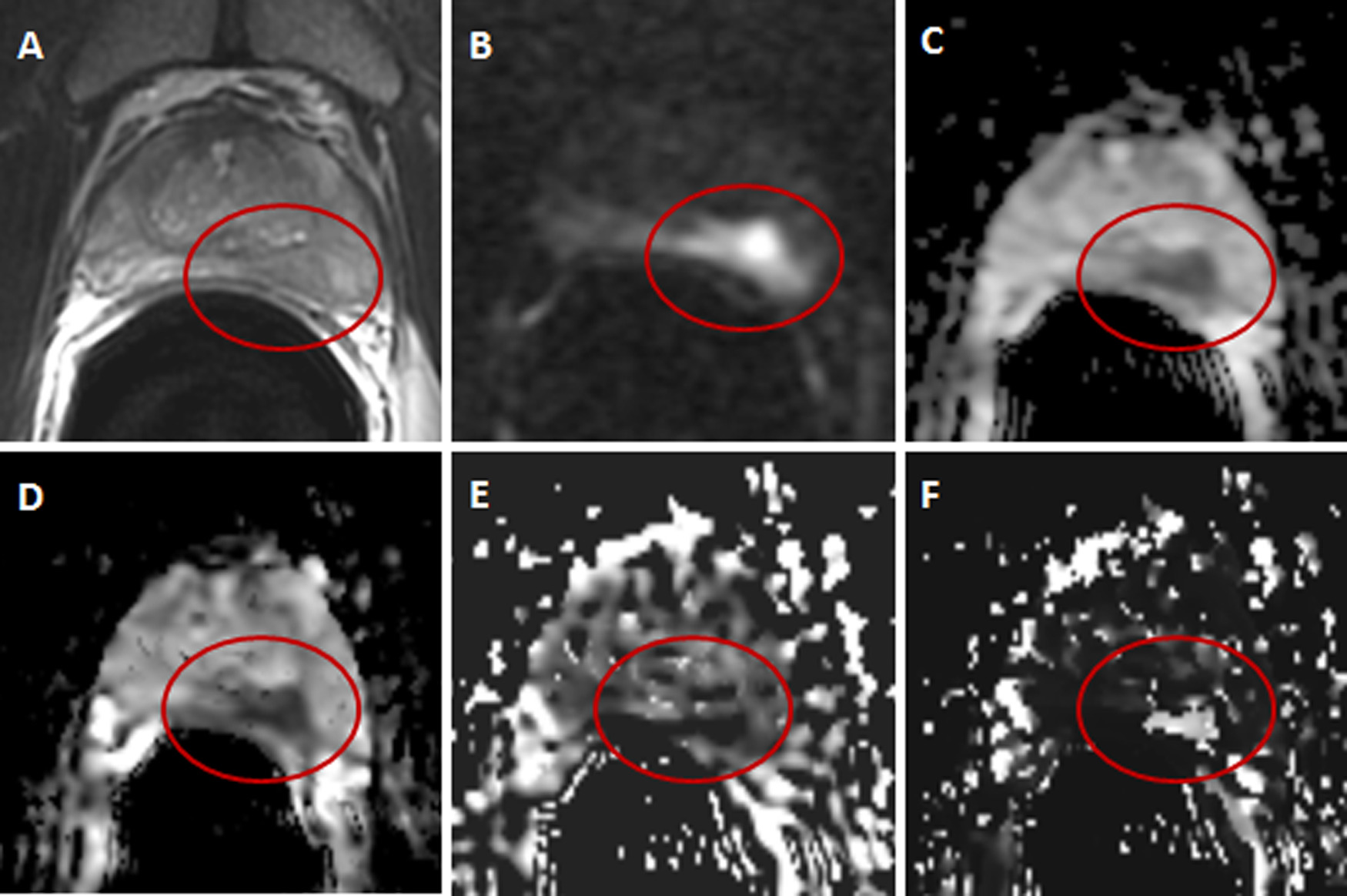
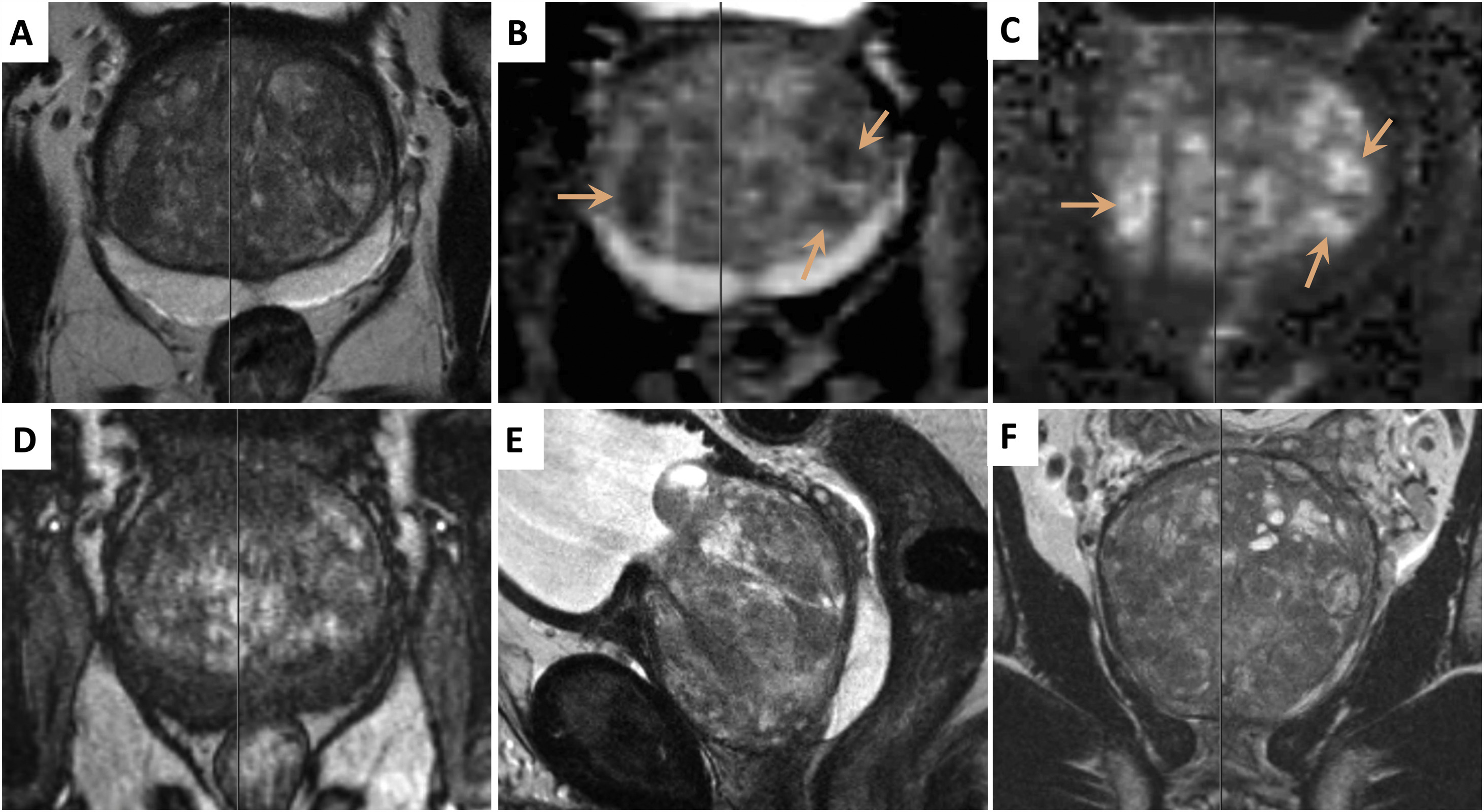
MRI SCAN (3T MULTIPARAMETRIC)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a type of scan that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of the body.
-
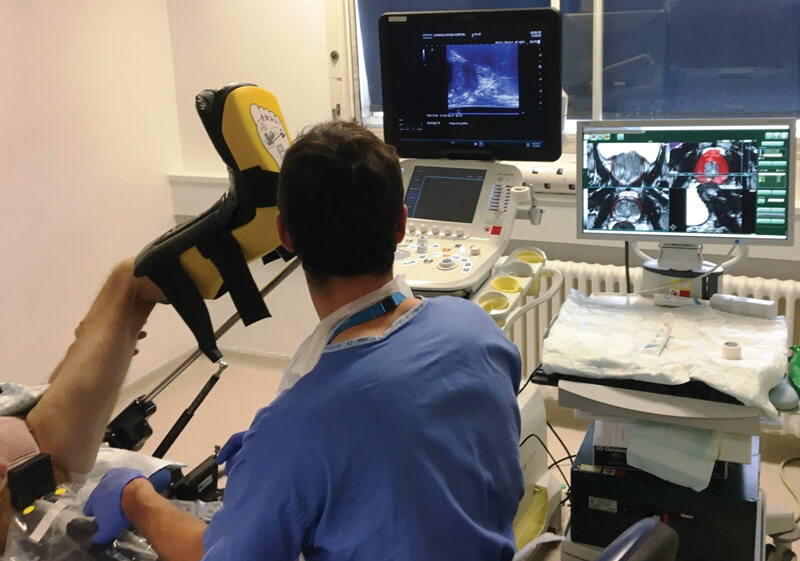
Transperinal & MRI Fusion guided biopsies
Template guided prostate biopsies or template prostate mapping (TPM) is used as part of the diagnosis for prostate cancer.
Bladder cancer diagnostics & treatments
-

Flexible Cystoscopy
Local anaesthetic assessment to visualise the inner lining of the bladder and diagnose the size and location of bladder tumours.
-
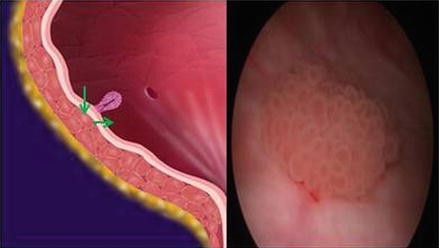
Transurethral resection of bladder tumors (TURBT)
During the telescopic examination of the bladder (cystoscopy), bladder tumours are ‘shaved’ or resected from the inside of the bladder wall with the aim of removing the entire tumour.
Kidney & ureteric stones treatments
-
Imaging & Biochemical Assesments
Kidney stones are increasingly common and unfortunately can be very painful. Accurate assessments of stone burden using ultrasound or CT imaging allows for a tailored management approach for each patient.
-
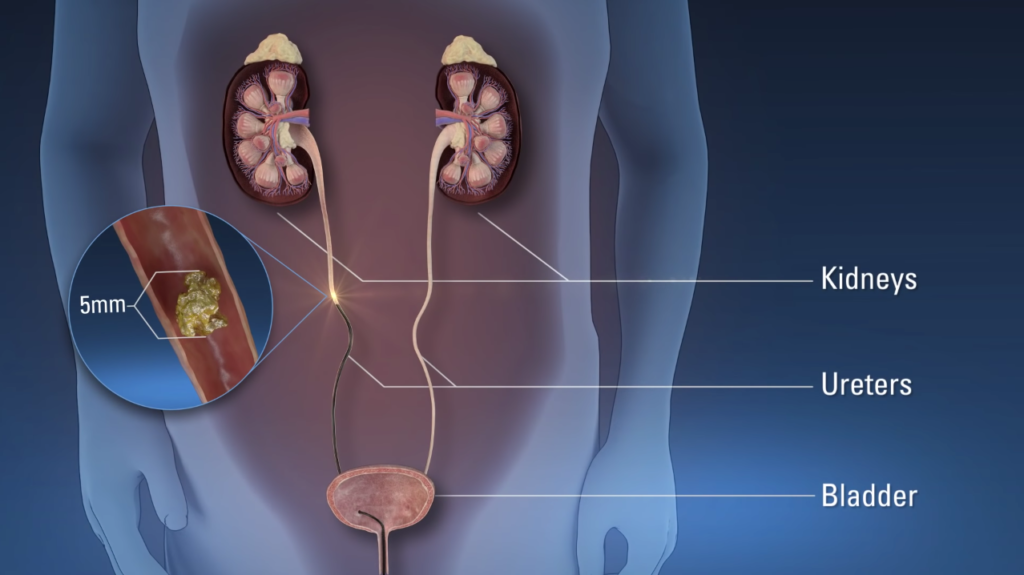
Shockwave Treatments & Laser Ureteroscopy
ESWL involves treating a stone in the kidney or ureter without the need for a general anaesthetic. Surgical intervention (ureteroscopy) allows small telescopes equipped with laser fibres to access, fragment and treat stones within the ureter or the kidney often as a daycase procedure.
Other Urological Treatments & Procedures
-

Circumcision
Circumcision involves the removal of the foreskin and is performed for medical or religious reasons. The procedure may be performed under general or local anaesthetic. Healing takes 4-6 weeks and there may be some swelling particularly in the first few days.
-
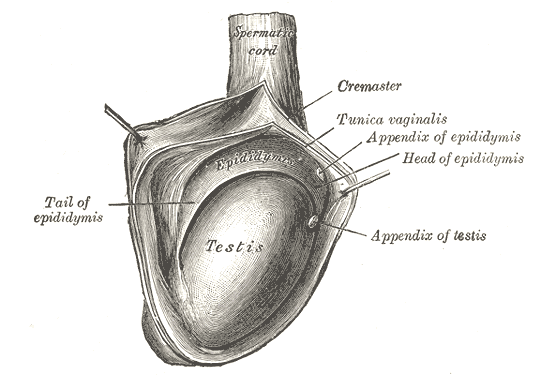
Jaboulay Procedure
An operation to repair a hydrocele involving excision and eversion of the hydrocoele sac. This procedure is typically performed as a daycase under general or local anaesthesia employing an incision through the scrotum.
-
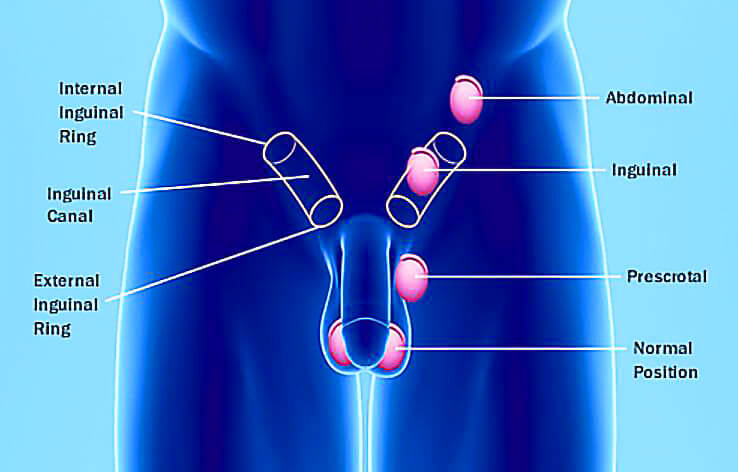
Orchidopexy
This is fixation of the testis (or testicle). If performed in young children/ babies for undescended testis, the procedure is performed via a skin incision in the groin. If performed to stop the testis twisting (testicular torsion) it is via an incision in the scrotal skin.
-
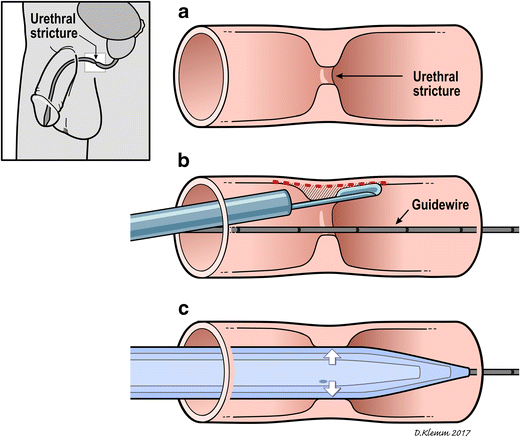
Urethral Dilation & Urethromoty
Dilatation involves graduated gentle stretching of the urethra, either in the management of male urethral stricture or in women for a wide range of conditions including urethral syndrome and recurrent cystitis. For more extensive narrowings, urethrotomy involves incising scarred narrowings and strictures.
-
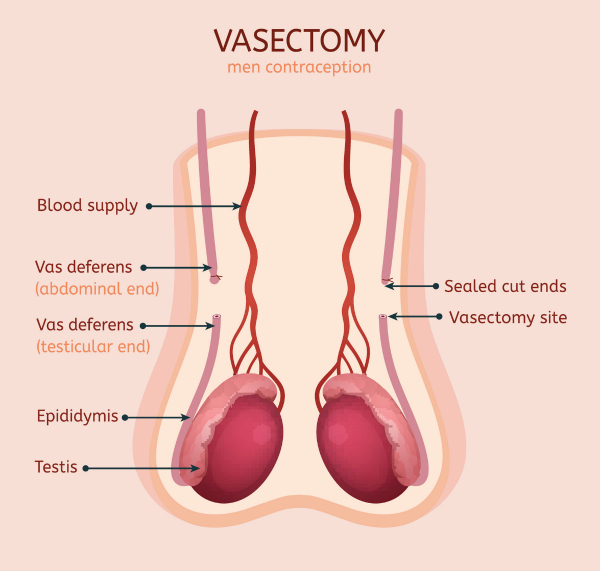
Vasectomy
Vasectomy is probably one of the most effective contraceptive options available today. Either under general or more usually a local anaesthetic block, the drainage tubes from the testicles (vas deferens) are located and disconnected through small incisions of the scrotum.
Book an Appointment
Contact us during office hours at our clinics
Specialist Medical Clinic+350 200 49999
MidTown Medical Clinic+350 200 62222
HC Marbella Hospital+34 952 90 86 28
Or for an emergency consultation 24/7
James Allan+44 7984 292 776
Or email uscontact@theurologyclinic.gi
- LUTS
- BPH
- Prostate cancer
- Bladder cancer
- Kidney stones
- Ureteric stones
- Circumcision
- Vasectomy
- Kidney stones
- Bladder cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Enlarged prostate
- Incontinence
- Ureteric stones
- Circumcision
- Vasectomy
